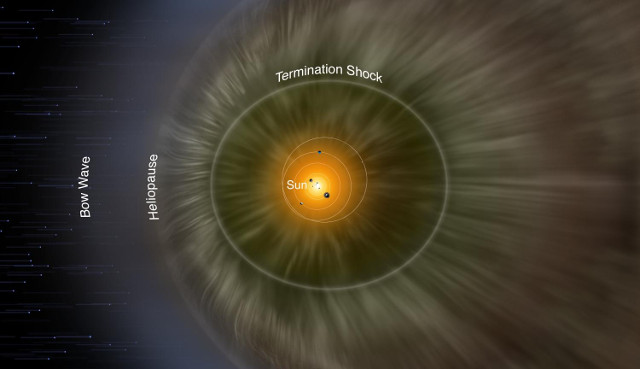
High pressure at the borders of interstellar space
A team of scientists led by Jamie Rankin of Princeton used measurements of the galactic cosmic rays detected by NASA’s Voyager space probes to obtain an estimate of the total pressure that plasma, magnetic fields and various particles exert on each other in the heliosheath, the outer region of the heliosphere, the big bubble around the Sun where solar wind exerts its influence. The result is higher than expected and will help to better understand the interactions between the Sun and its surroundings.

