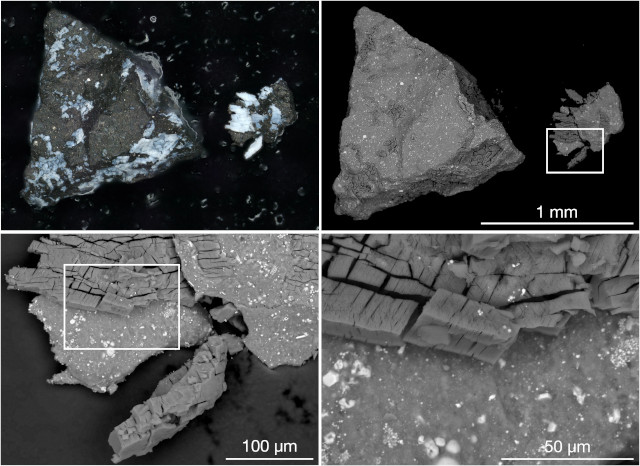
DNA and RNA bases and several amino acids found in samples from asteroid Bennu
Two articles, one published in the journal “Nature” and one in “Nature Astronomy” report the results of examinations of samples from asteroid Bennu with the discovery of the presence of all the DNA and RNA bases and 14 of the 20 amino acids present on Earth. Two teams of researchers analyzed these samples, which were collected by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx space probe, which brought them back to Earth. Building blocks of life were also found in samples from the asteroid Ryugu brought back to Earth by the Hayabusa 2 space probe and the ones found in the samples brought back from Bennu offer new confirmation that the Earth may have been “seeded” by asteroids.